Community resources
Community resources
Community resources
The Kanban Methodology and why you need it for your Software Team!

Kanban (Japanese 看板, signboard, or billboard) is a lean method to manage and improve work across human systems. This approach aims to manage work by balancing demands with available capacity, and by improving the handling of system-level bottlenecks. — wikipedia
In Project and Product Management, Kanban utilizes the power of visualization to increase team efficiency and deliver value to the team and customers faster. A kanban board can be used to visualise work, limit work-in-progress, and maximize efficiency (or flow). Kanban boards use a board, cards, columns, and continuous improvement to help technology and service teams commit to the right amount of work, and get it done!
The Goal
The main goal of a team using Kanban is to take cards/tickets from the commitment point(BACKLOG) to the delivery(DONE) point as fast as possible. The elapsed time between these points is called Lead Time. So we can say that the main goal here is to reduce the lead time as much as possible.
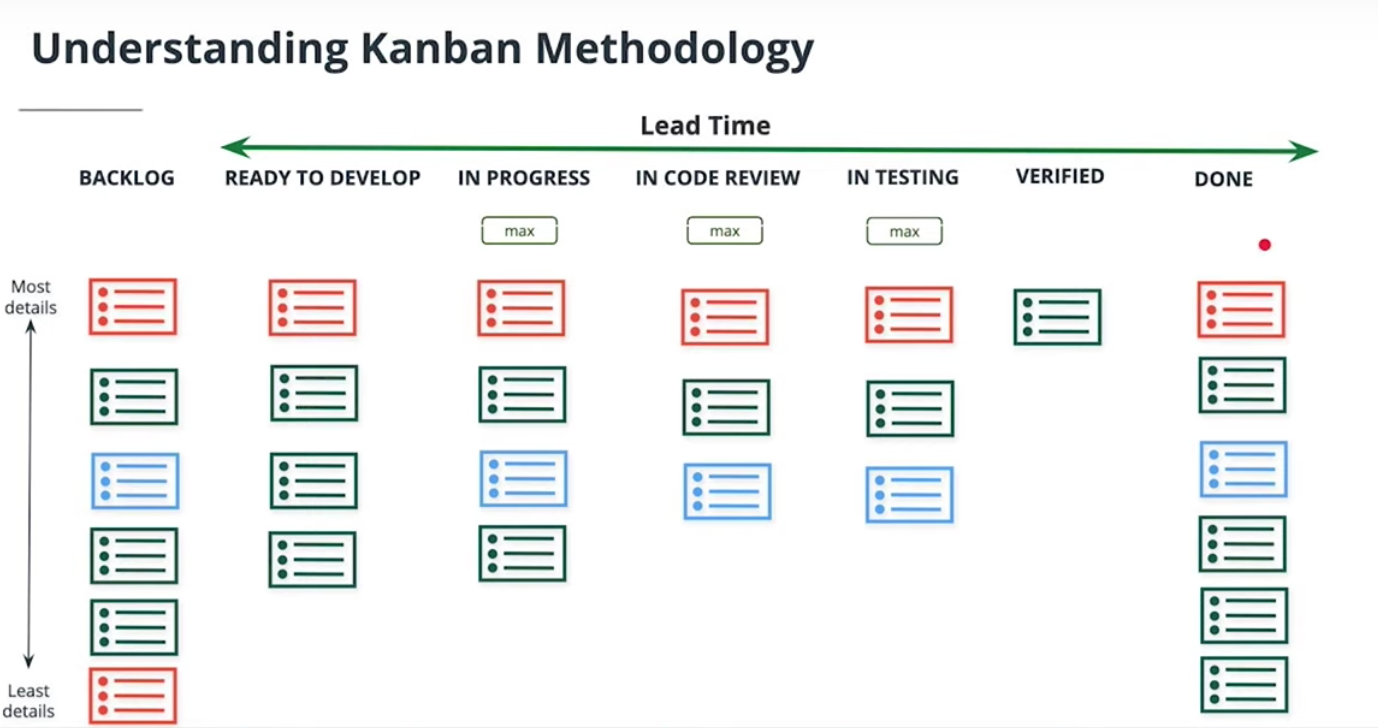
How the Kanban Framework works
Understanding the Components of the Kanban framework and how they work is set to lead your team to better project workflows and product launches.
The image above describes the basic components of the Kanban framework which are;
- Visual Signal: Kanban makes it very easy for every team member and stakeholder to easily visualize and understand the status of each task/ticket, who is doing what, blockers, etc. This is usually achieved by the use of tickets or stickies. In general, these visuals make it easy for teammates to understand quickly what the team is working on.
- Columns: This is another important component of the Kanban. each column represents a workflow with tickets in it. Depending on your team workflow and style, the most basic workflows are; TO DO, IN-PROGRESS, and DONE. Tickets or cards flow through the workflow until completed. These tickets are mostly containing the tasks which are usually “user stories” and must be assigned to a person
- Work In Progress (WIP) Limits: The Kanban methodology enables teams to set what is called WIP. This is used to avoid “bottlenecks”. For example, a column that has a WIP of 4 must have the team member(s) responsible for the tickets in that column finish those 4 tickets and move them forward before another ticket or card will be able to be added to the column.
- Commitment point: In a typical Agile team using Kanban, there’s always a “backlog” from where teammates keep ideas and pick them up for execution. The commitment point is the exact time when an idea is taken from the backlog and the team starts working on it.
- Delivery Point: As an Agile team member, always remember that the goal of the team is to get work DONE and minimize the LEAD TIME, ie. moving ticket(s) from the left side(commitment point) of the board to the very last column of the right side. The delivery point is the end of the Kanban team’s workflow. At this point, the customer must have validated the work and is happy with it.
Types of Kanban Boards
- Physical Kanban Board
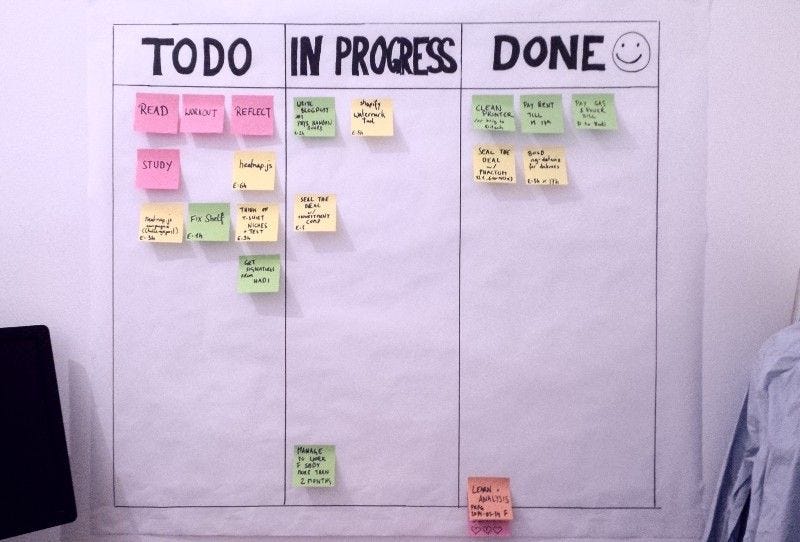
Physical Kanban Boards are easier and do not need any technical skills to setup and is ideal for teams who are in the same physical location, just with your white or black board, marker, stickies, and eraser, you can have your Kanban board. However physical boards are not ideal for remote and software teams since team member(s) will at some point be distributed or remote.
Digital or Electronic Kanban Boards
Kanban boards went through a digital transformation when the Kanban Methodology started gaining favor with Engineering and Software teams. Digital boards allow teams that do not share physical office space to use kanban boards remotely and asynchronously. The electronic board has many advantages over the traditional board. Advantages include; ability to be used by remote/distributes teams, the ability to customize to contain many features, ability to integrate with other engineering tools like Slack, Git, etc. To use an electronic Kanban Board, you will need software( I will talk about my favorite Kanban Software — Jira from Atlassian and how to use it in my next article), a product or project manager who will set it up and oversee things on a high level, assignees who will handle each task or deliverable.
In as much Kanban boards have undergone digital transformation, I still recommend you use both the traditional board and the digital board. The traditional or physical board will promote physical team communication at the workplace for team members who are at the same place. Actually, I still use it professionally alongside the digital Kanban Board.
Why do you need to use the Kanban Methodology?
- Self-organizing
- Transparency
- Accountability
- Collaboration
- Increased Productivity
- Predictability
- Reduced Waste
- Flexibility
- Bottle Neck Management
Among the listed advantages, I find the self organising point very dear. As a project manager, I don’t always have to move the tickets myself, other team members are responsible for each task they have been assigned to and failure to move for example a ticket(s) that is supposed to be “IN LOCAL DEV” means that she/he is not working on anything even when they are actually working. That sense of responsibility it gives everyone is something huge, and then it does not stop there, It goes further to be transparent for everyone to see, you even get alerts in your communication tools like Slack for every update on the board(digital board).
Oh wow, you made it to this point, thanks for taking out time to read. At this point, you must have understood what Kanban is and why it is very necessary for your software team. However, if you are interested in setting it up and using it for your team or any other question(s), you can send me a DM on Twitter @tech_bella or send me an email on Gmail. Don’t forget to leave comments in the response section regarding any other thing.
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Gloria Ojukwu
4 comments