Community resources
Community resources
Community resources
Using Jira REST API URLs to Access Data
In my last article, I shared an easy way to find what you’re looking for by changing parameters in URLs in your browser’s address bar. This time, let’s explore accessing Jira information using REST API URLs.
What is a REST API?
Briefly, REST stands for representational state transfer and API means application programming interface. A REST (sometimes called RESTful) API allows multiple systems to exchange information or share data. For example, third-party apps from the Atlassian Marketplace use Atlassian’s REST APIs to connect to Jira to provide additional features and functionality. Companies like Atlassian make APIs available so others can leverage, integrate with, and connect to their systems. Atlassian offers APIs for their different products (e.g., Jira Software, Jira Service Management, and Confluence) and different deployment types (e.g., Cloud and Data Center). More information is available in the developer documentation at developer.atlassian.com.
But I’m Not a Software Developer!
Even if you’re not developing your own custom features and building apps you can still leverage the REST APIs to access Jira data. You don’t need any special programming skills to use the information below. Just make sure you’re logged in to Jira when pasting URLs in your browser’s address bar.
And don’t worry, the REST API respects all permission settings. This trick does not expose information users can’t already access in Jira.
Easy Example
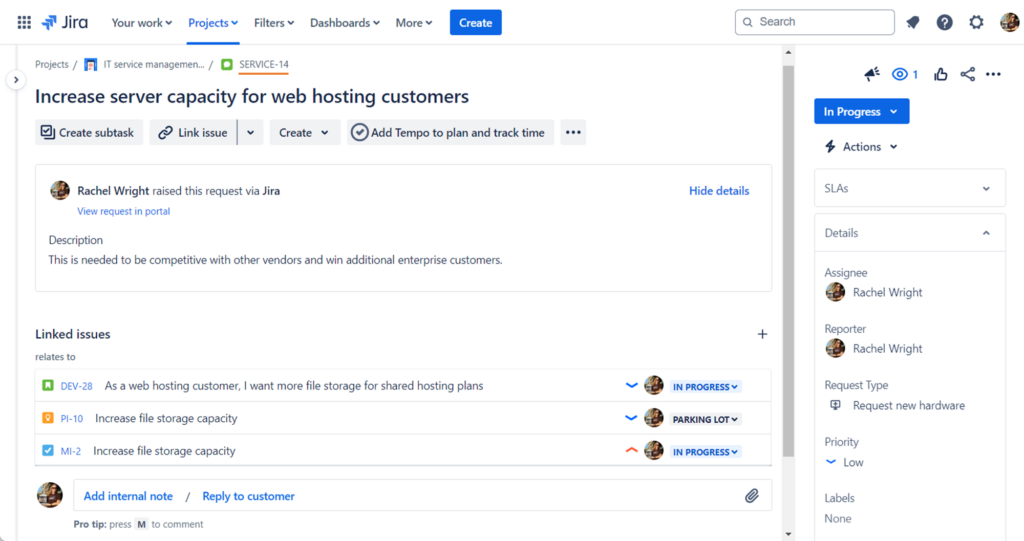
This screenshot shows a Jira issue in a Service Management project with the key SERVICE-14. Use the URL format below to get issue configuration information, like custom field names.
| Format: | your-jira-URL/rest/api/latest/issue/ISSUE-KEY?expand=names |
| Example: | your-jira-URL/rest/api/latest/issue/SERVICE-14?expand=names |
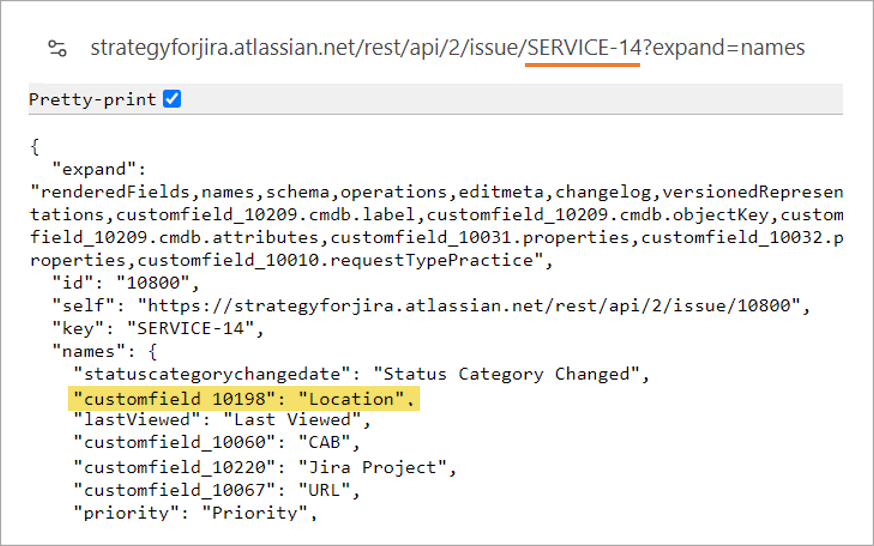
The second screenshot shows the information returned when embedding SERVICE-14 in the sample URL. For example, a custom field named “Location” is shown and its unique ID is 10198. I can use that ID in an automation rule, in a JQL query, in a script, and more.
Jira URLs
Here are some example URLs to try in your browser’s address bar. Simply prepend your Jira URL and change the bolded parameters.
Users
Cloud
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/user?accountId=ACCOUNT-ID |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/user?accountId=6e6feca20a6a810c48 |
Tip: In Cloud, usernames are formatted as long strings of letters and numbers. They are set by Atlassian. There’s no way to change them and they are used across Cloud sites and products.
Server and Data Center
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/user?username=USERNAME |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/user?username=rwright |
Tip: In Server and Data Center, username format are customizable. They are generally in the format “first.last”, “flast”, or sometimes they are an email address.
Issues
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/issue/ISSUE-KEY?expand=names |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/issue/SERVICE-14?expand=names |
Projects
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/project/PROJECT-ID |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/project/10056 |
Tip: Use “/rest/api/latest/project” to get a list of all projects. Use this format to get lists of other objects too, like dashboards or resolutions, for example.
Boards
| Format: | /rest/agile/latest/board/BOARD-ID |
| Example: | /rest/agile/latest/board/17 |
Dashboards
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/dashboard/DASHBOARD-ID |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/dashboard/10000 TIP: ID 10000 is the default system dashboard |
Filters
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/filter/FILTER-ID |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/filter/10057 |
JQL Keyword Search
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/search?jql=text%20~%20″KEYWORD“ |
| Example: | /rest/api/latest/search?jql=text%20~%20″website%20error“ |
Tips:
- Use “%20” to represent a space in a URL. For additional character codes, see: HTML URL Encoding Reference.
- In JQL, use the format “text ~ keyword” to find issues that contain specific keywords in an issue’s summary, description, or comment fields.
JQL Query
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/search?jql=JQL-QUERY |
| Example: For the JQL query “project = dev and status = done” | /rest/api/latest/search?jql=project=dev%20and%20status=done |
Statuses
| Format: | /rest/api/latest/status |
Documentation
For the full list of examples and capabilities, see:
- Cloud – https://developer.atlassian.com/cloud/jira/platform/rest
- Server and Data Center – https://developer.atlassian.com/server/jira/platform/rest/
Have additional examples to share? Post them below!
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Rachel Wright
About this author
Author, Jira Strategy Admin Workbook
Industry Templates, LLC
Traveling the USA in an RV
47 accepted answers
2 comments