Community resources
Community resources
Community resources
How to anonymize Jira projects before the export
Perhaps you are migrating from one server to another, or you want to send a project to the support service without sensitive personal data: The reasons for wanting to anonymize and then export Jira projects are many and varied.
In this practical step-by-step guide, we explain to you how to handle this easily and straightforwardly with GDPR (DSGVO) and Security for Jira.
Anonymize Jira projects before the export: step-by-step
Before you start anonymizing, you should note that anonymizing is an irreversible process. So if you want to share your project information with someone, but still need it for editing yourself, you should duplicate the project first.
As you can see in the Atlassian documentation, Atlassian itself does not offer a built-in tool to copy entire projects. However, in the Marketplace, you will find a variety of apps that can be used to solve this problem.
If you did some kind of backup and your data is safe, you can start with anonymizing your projects.
1. Create a dummy user
When anonymizing the Jira project, we will replace the users along with their personal data with a dummy user. Either you already have a fictitious user for such purposes, or you create one.
To do this, navigate to Add User in the user module and enter a username. In our example, we use the name user_for_anonyzation.
This dummy user behaves in the project like a real user, but has no sensitive private data. Therefore, it is perfect for our project.
2. Anonymize a complete Jira project
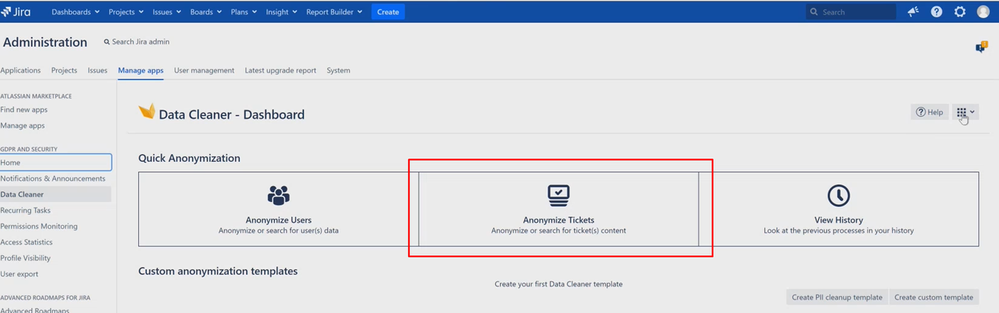
Step 1: From the Jira Dashboard, navigate to the GDPR Tool, then to the Data Cleaner Dashboard and select the Anonymize Content module.
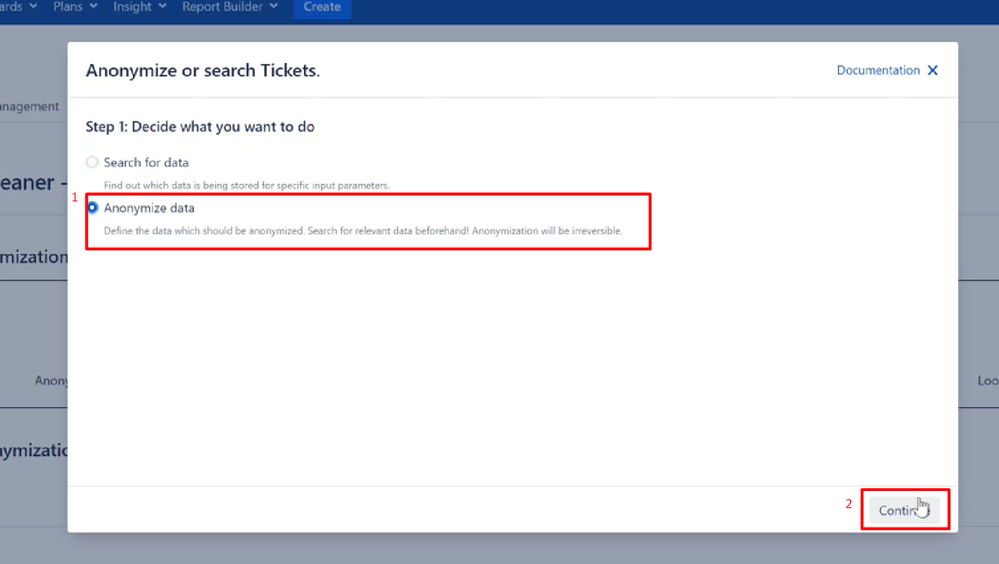
Step 2: If you prefer to be on the safe side with anonymization, you can first select Search for data and then click on Continue.
You can also choose Anonymize Data directly. If you select option 1, you will end up with a result that is not processed. If you pick the direct anonymization, you will end up with search results that are processed.
Regardless of which option you select, the following steps are identical:
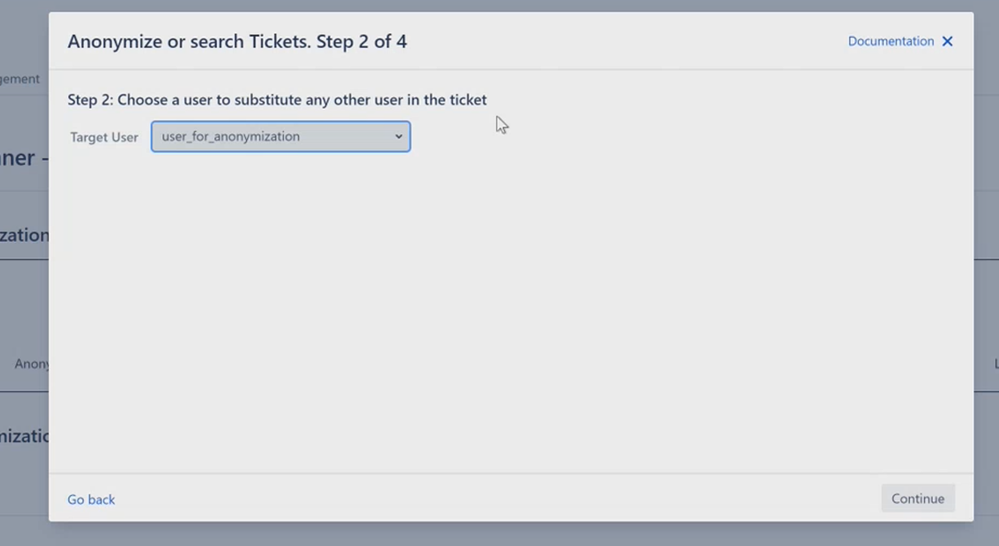
Step 3: In the next step, select the dummy user you created earlier as the Target User, which will then replace all other user data. Click on Continue.
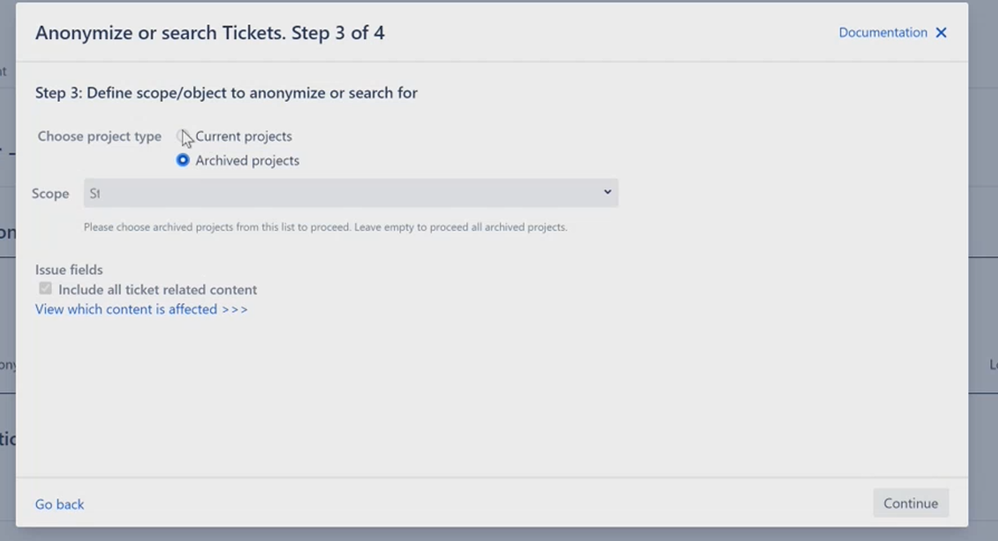
Step 4: The next step shows one of the highlights of our tool: You can even edit projects that have already been archived.
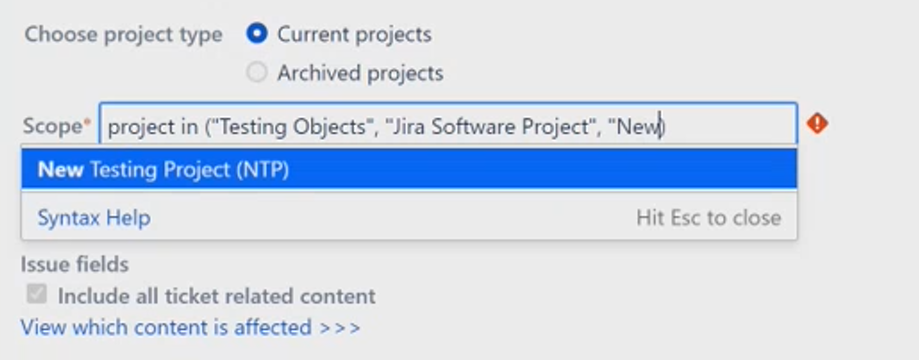
You define the scope here with JQL, the Jira Query Language. Be sure to check Atlassian's JQL documentation to know the best practices.
Keep in mind that you can’t find archived Jira projects using JQL. To select them in the scope, you have to find out their key or the name.
To work with existing projects, click on Current projects.
Here, you can choose as many projects as you like:
Then, choose Continue.
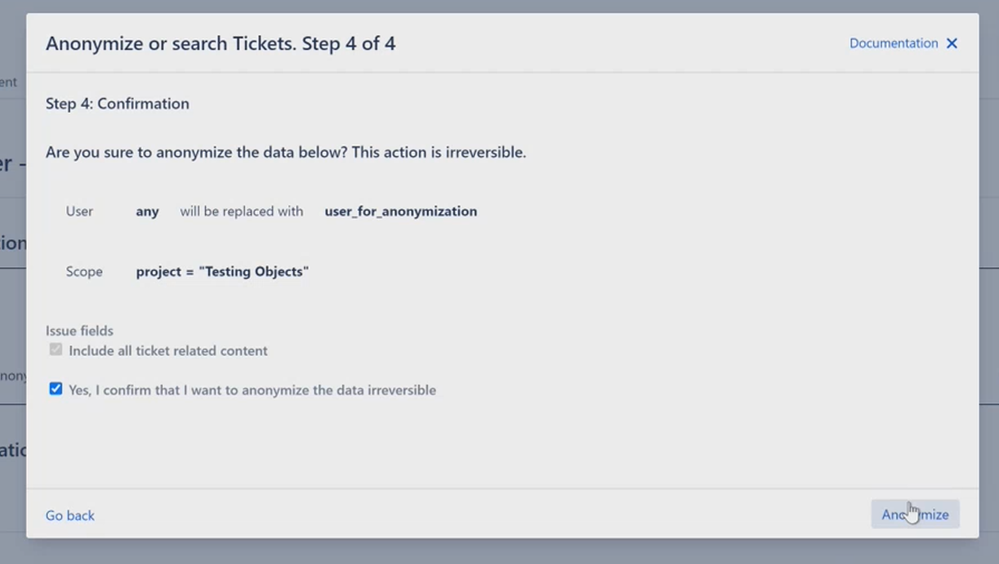
Step 5: The following screen gives you an overview of the upcoming action. In the project named "Testing Objects", each user will be replaced by user_for_anonymzation.
Please also confirm that you are aware of the irreversibility of the anonymization. Then click on Anonymize.
If you have selected method 1 before and want to see search results first, the Search button will appear at this point. Click this button.
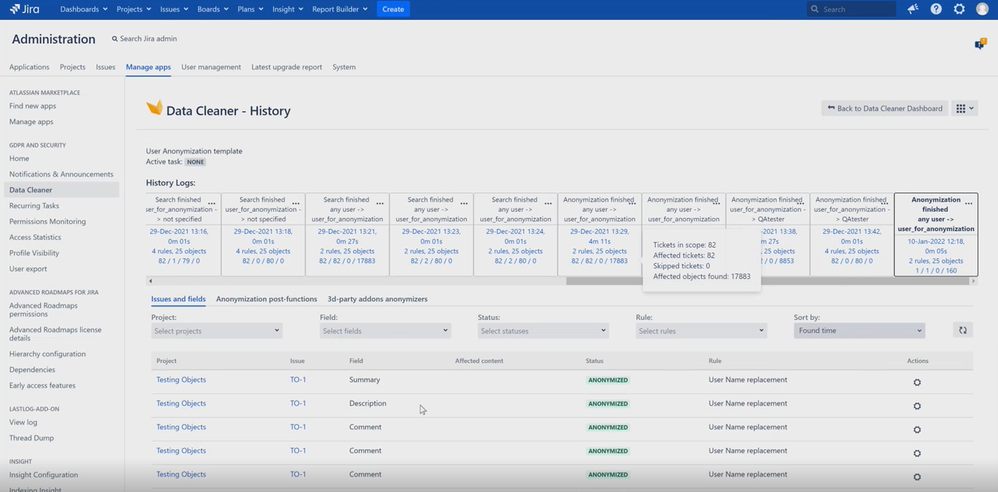
Step 6: After the anonymization is complete, the Data Cleaner History is automatically displayed. Here, you have the perfect overview of exactly which data was anonymized.
Now, all data is anonymous, and you can share Jira projects as you like!
3. Export your Jira project
Unfortunately, Atlassian's Jira still does not offer a comprehensive export function for projects. To perform the export successfully, you may need another tool from the Marketplace. You can find some instructions in the Atlassian documentation.
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Andreas Springer _Actonic_
About this author
Head of Marketing
Actonic GmbH
Germany
2 accepted answers
Atlassian Community Events
- FAQ
- Community Guidelines
- About
- Privacy policy
- Notice at Collection
- Terms of use
- © 2025 Atlassian






0 comments