Community resources
Community resources
Community resources
5 Steps to Assessing Security Vulnerabilities in Jira using the CVSS Framework
What is CVSS and when to use it?
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a standardized framework for rating the severity of security vulnerabilities. The CVSS was developed and is maintained by the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST). FIRST is an international consortium that aims to foster cooperation and coordination in incident prevention and response, as well as to promote the sharing of information among member organizations.
The CVSS provides a numerical score that reflects the potential risk posed by a vulnerability. CVSS scores range from 0.0 to 10.0, with higher scores indicating more severe vulnerabilities. The scoring is based on a set of metrics that evaluate the exploitability and impact of the vulnerability. By applying the CVSS metrics, you can accurately assess the risk posed by the vulnerabilities and take appropriate actions to mitigate them.
CVSS is widely used across various industries, but it is particularly prevalent in the information technology (IT) and cybersecurity sectors of regulated domains like the financial industry, telecommunications, public and defence sectors as well as the healthcare domain.
Scoring a Security Vulnerability Using CVSS 4.0 in Jira
The CVSS version 4.0 introduces enhancements that make it easier to evaluate and communicate the risk of vulnerabilities. Here's a step-by-step tutorial on how to score a security vulnerability using CVSS 4.0.
The CVSS score is a newly released feature of the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus app on Jira Cloud. To start, make sure you have the Risk Manager Plus app installed and you have created a project, assigned a risk model to it. Tutorial on setting up and configuring the Risk Manager Plus for CVSS can be viewed here.
You can also check out the video tutorial on how to set up CVSS in Jira:
Step 1: Get Acquainted with the CVSS Metrics
The CVSS metrics is used to score the level of severity of the vulnerabilities across various characteristic groups and impact metrics on how the vulnerability can be exploited (CIA), including the required access level and complexity of the attack.
CVSS 4.0 uses four groups of metrics to evaluate vulnerabilities:
- Base Metrics: These represent the intrinsic characteristics of a vulnerability that are constant over time and user environments. They are divided into two categories:
- Exploitability Metrics: These measure the ease and technical means by which the vulnerability can be exploited.
- Attack Vector (AV)
- Attack Complexity (AC)
- Privileges Required (PR)
- User Interaction (UI)
- Impact Metrics: These measure the direct consequence of a successful exploit on the impacted component.
- Confidentiality (C)
- Integrity (I)
- Availability (A)
- Exploitability Metrics: These measure the ease and technical means by which the vulnerability can be exploited.
- Supplemental Metrics: These measure aspects of a vulnerability that can change over time but not across user environments.
- Safety (S)
- Automatable (AU)
- Recovery (R)
- Value Density (V)
- Vulnerability Reponse Effort (RE)
- Provider Urgency (U)
- Environmental (Security) Metrics: These measure the characteristics of a vulnerability that are relevant and unique to a particular user’s environment.
- Confidentiality Requirement (CR)
- Integrity Requirement (IR)
- Availability Requirement (AR)
- Modified Base Metrics (similar to the Base Metrics but tailored to the user’s environment)
- Threat Metrics: These measure the likelihood of the vulnerability being attacked, and is based on the current state of exploit techniques and exploit code availability.
- Attacked (A)
- Proof-of-Concept (P)
- Unreported (U)
Step 2: Evaluate Base Metrics
To score the Base Metrics, evaluate the following:
- Attack Vector (AV): Determine how the vulnerability is accessed and its context. Options include Network (N), Adjacent (A), Local (L), and Physical (P).
- Attack Complexity (AC): Assess the conditions beyond the attacker's control that must be present for exploitation. Options are Low (L) and High (H).
- Privileges Required (PR): Identify the level of privileges an attacker must have to exploit the vulnerability. Options are None (N), Low (L), and High (H).
- User Interaction (UI): Determine if user interaction is required for exploitation. Options are None (N) and Required (R).
- Confidentiality (C), Integrity (I), Availability (A): Rate the impact on these areas as None (N), Low (L), or High (H).
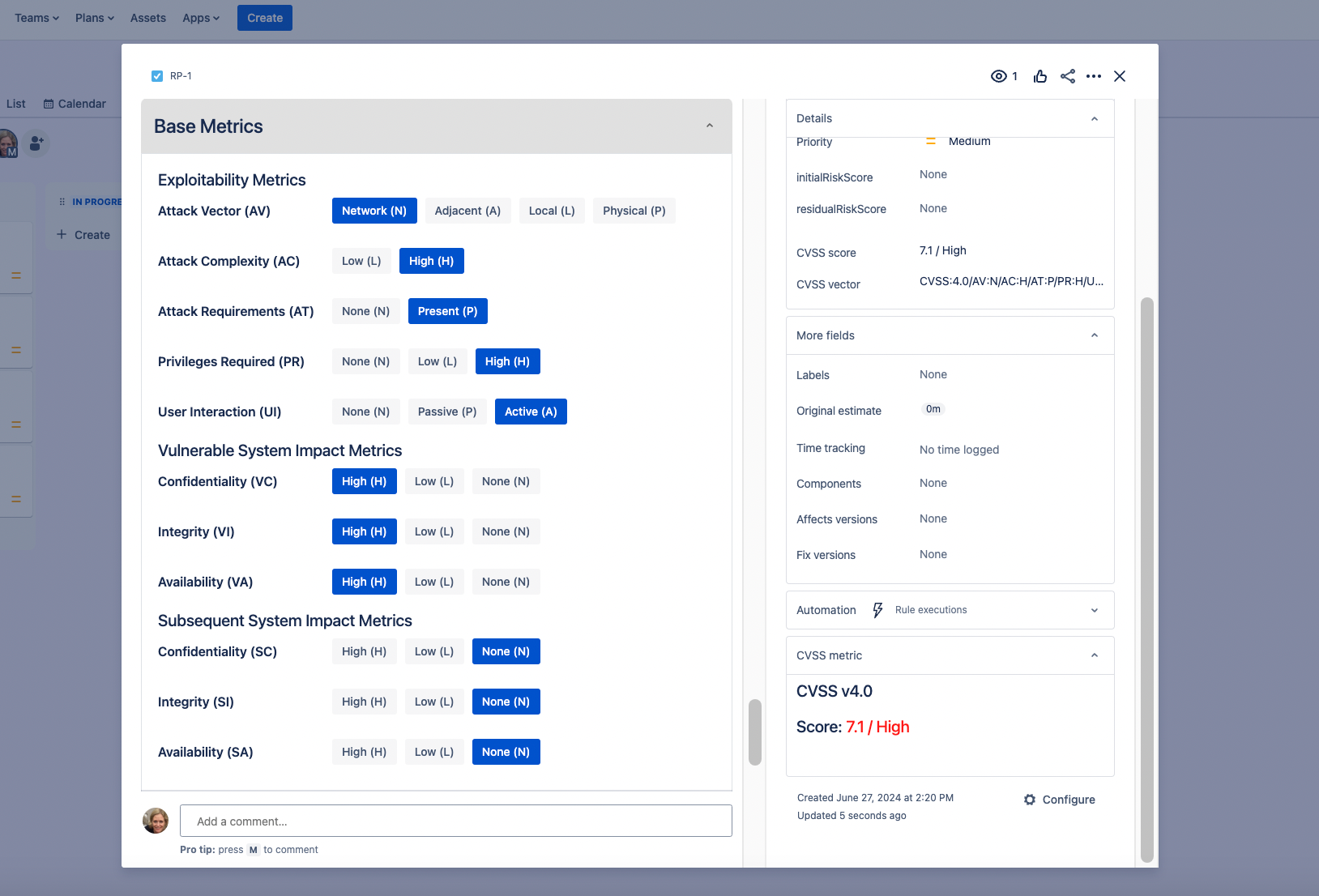
Step 3: Evaluate Supplemental, Environmental and Threat Metrics
- Supplemental Metrics: Assess the current state of safety, recovery, available response effort, and the urgency of the reported vulnerability.
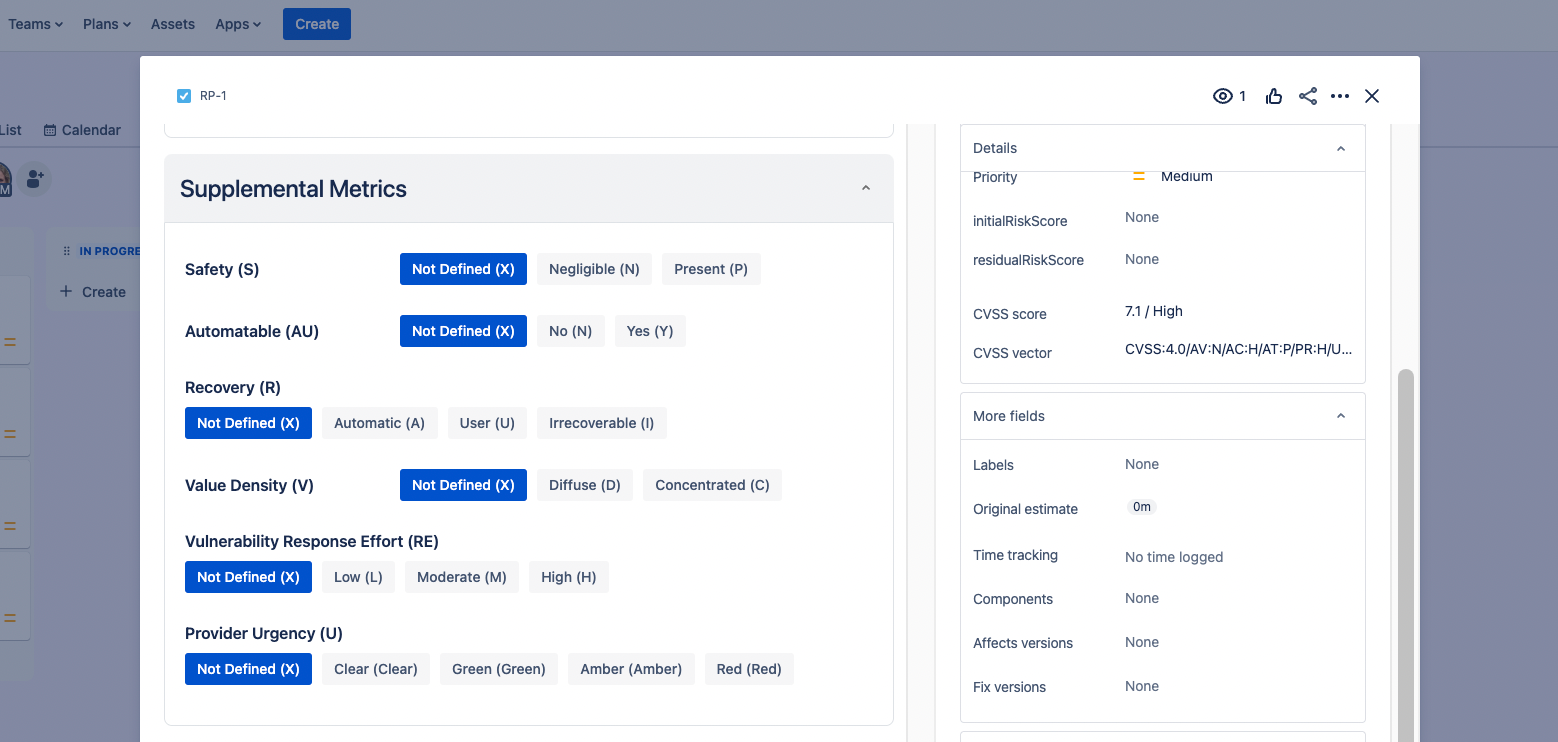
- Environmental Metrics: Adjust the Base Score based on the specific context of your environment. This includes reassessing the impact metrics and requirements.
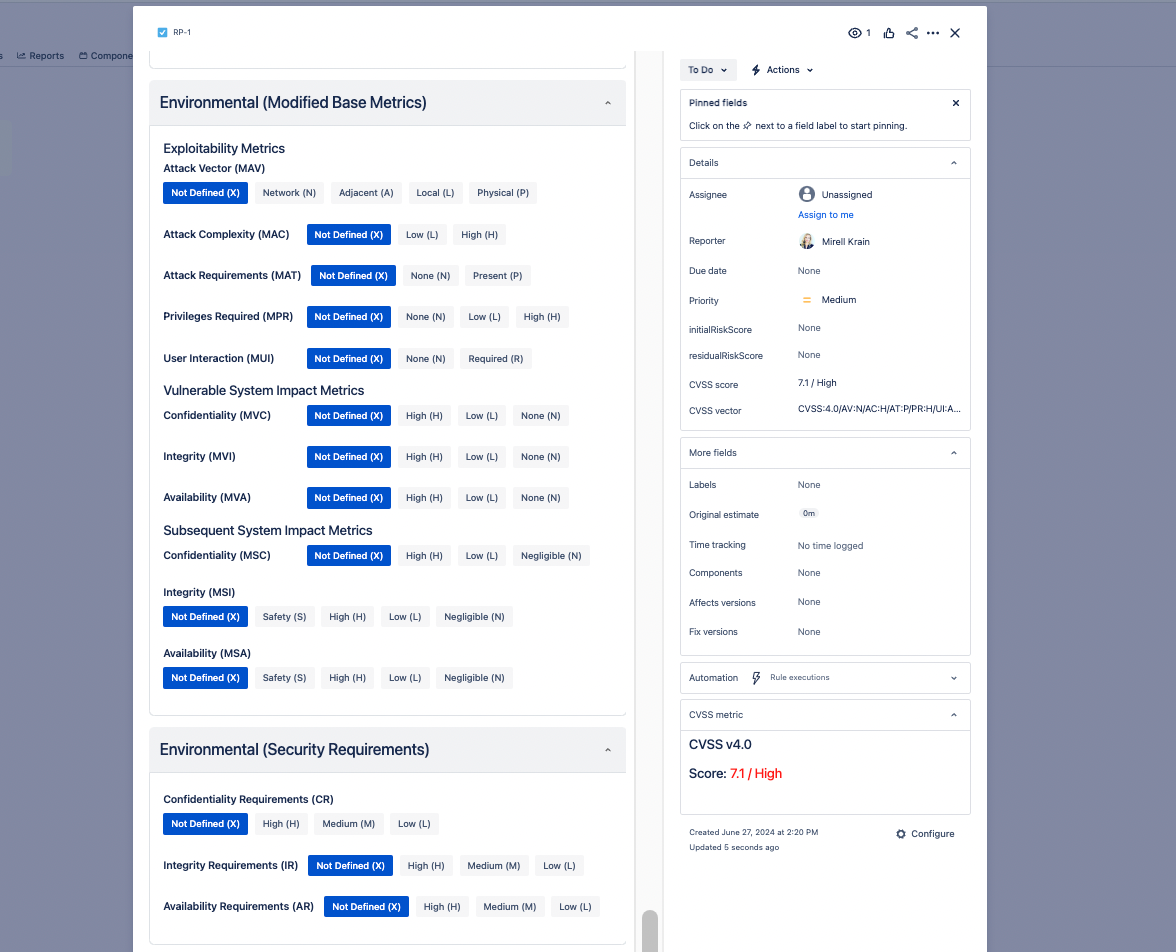
- Threat metrics measure the likelihood of the vulnerability being attacked, and is based on the current state of exploit techniques and exploit code availability.
Step 4: Overall CVSS Score
The Risk Manager Plus app on Jira combines the Base, Supplemental, Environmental and Threat scores to obtain the final CVSS score. This score gives a comprehensive view of the vulnerability's severity and helps prioritize remediation efforts. The formula provides a score between 0.0 and 10.0.
Step 5: Vulnerabilities as Jira issues
Now that you know what exactly you need to score for each identified vulnerability, you can start by creating them as Jira issues, define their Jira issue type and add all the necessary information to them.
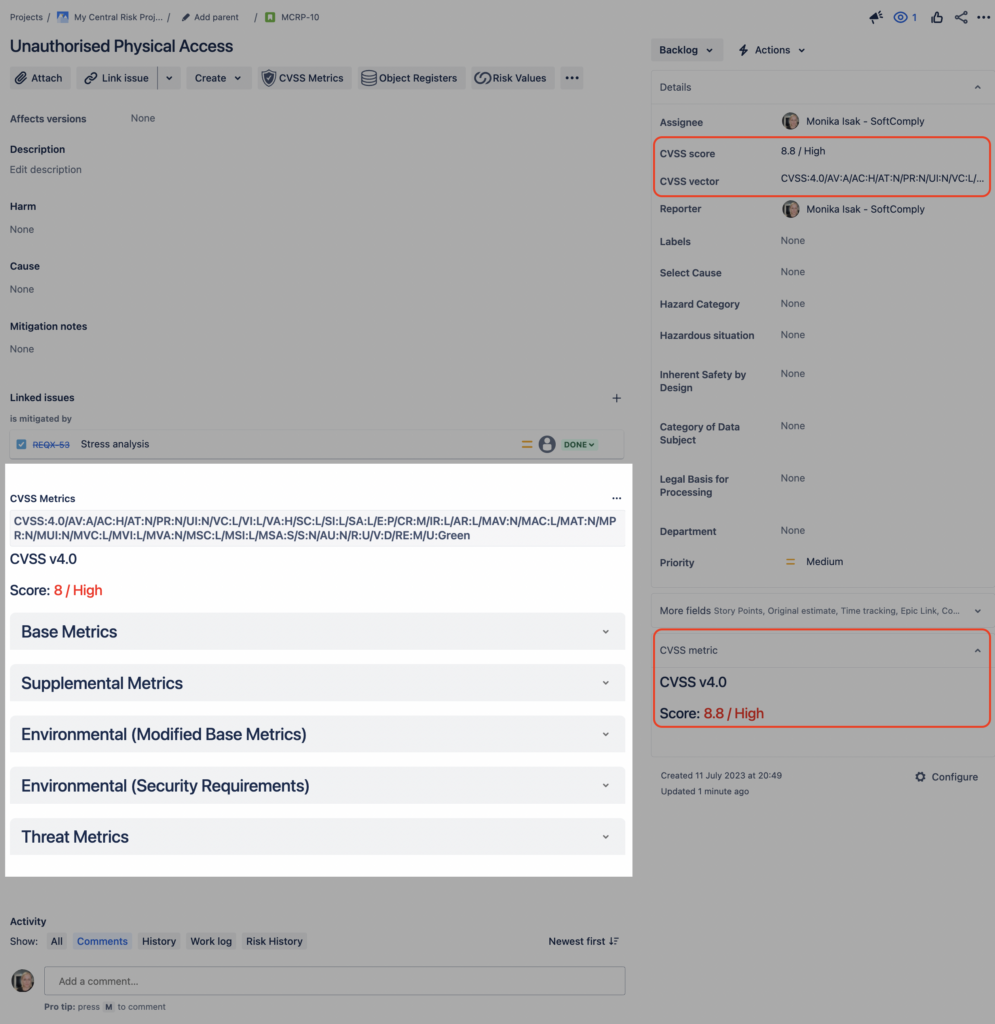
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) Metrics in Jira enhances your ability to monitor, prioritize, and manage security vulnerabilities within your Jira environment.
After setting up and configuring the CVSS metrics in the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus, you will have the CVSS Score & CVSS Vector visible in a Jira Issue view.
Summary
Scoring security vulnerabilities provides several significant benefits that enhance the overall security posture of an organization:
- Prioritisation of necessary remediation actions: Based on the CVSS score, you can target the high-severity vulnerabilities, that pose a greater risk, first to mitigate the most critical threats.
- Ensuring compliance: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards require organizations to assess and manage security vulnerabilities. Using a recognized scoring system like CVSS helps you meet compliance requirements and provides a structured way to document and report vulnerability management activities.
- CVSS as an integrated part of your Risk Management: Scoring vulnerabilities contributes to the your overall risk management strategy. It allows for a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks, which is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
- Consistency when working with Vendors and Partners: When working with vendors and partners, a common scoring system helps in assessing and comparing the security risks associated with third-party products and services. It also aids in setting expectations and requirements for security practices.
👉 Try SoftComply Risk Manager Plus for free for a month: https://marketplace.atlassian.com/apps/1219692/softcomply-risk-manager-plus-top-risk-management-in-jira?tab=overview&hosting=cloud
👉 Book a live demo: https://calendly.com/softcomply/softcomply-risk-manager-demo
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Marion Lepmets _SoftComply_
About this author
CEO
SoftComply
Munich, Dublin, Tallinn
3 accepted answers
0 comments