Community resources
Community resources
Risk Management: Understanding ISO 31000
ISO 31000 is an international standard that provides guidelines and principles for creating a risk management framework and process. It offers a systematic approach for organizations to identify, assess, manage, and monitor risks to achieve their objectives, make informed decisions, and safeguard their assets. Although ISO 31000 is not attached to a formal certification process, it is a benchmark for organizations to design and implement risk management strategies, ensuring consistency, transparency, and effectiveness across different sectors and environments.
The standard consists of these sections:
- Scope
- Normative references
- Terms and definitions
- Principles
- Framework
- Process
Scope
The standard offers universal risk management guidelines suitable for any organization, regardless of industry, and applies to all activities and decision-making levels.
Normative references
Normative references are essential documents cited in a standard for its application; ISO 31000 contains none.
Terms and definitions
This section provides detailed definitions of essential terms related to risk management, ensuring clarity and consistency in their interpretation and application. For instance, "risk" is defined as the "effect of uncertainty on objectives," while a stakeholder is a "person or organization that can affect, be affected by, or perceive themselves to be affected by a decision or activity."
Principles
This section outlines the principles essential for effective risk management. The principles emphasize integrating risk management into all organizational activities and structuring it to be comprehensive and tailored to an organization's context. The approach should actively involve stakeholders, dynamically respond to changing contexts, and use the best available information. Moreover, the process should address human and cultural influences and continuously improve from learning and experience.
Framework
This section outlines the overarching elements required to implement effective organizational risk management. It covers various aspects such as leadership commitment, integration of risk management, design considerations, implementation processes, evaluation, and continuous improvement. It emphasizes the need for top management's active involvement, customization of the framework to the organization's context, allocation of resources, communication, and consultation strategies, as well as ongoing monitoring and adaptation to address changes. Successful implementation of this framework ensures that risk management becomes an integral part of organizational activities, decision-making processes, and overall governance, fostering a culture of proactive risk management to achieve objectives.
Process
This section outlines the risk management process, encompassing the systematic application of policies, procedures, and practices. The process involves several key steps: communication and consultation, establishing the scope, context, and criteria, risk assessment (including identification, analysis, and evaluation), risk treatment (including option selection, plan preparation, and implementation), monitoring and review, and recording and reporting. This process is iterative and dynamic, tailored to the organization's objectives and context. It emphasizes the importance of considering external and internal factors, engaging stakeholders, assessing risk comprehensively, selecting appropriate treatment options, and consistently monitoring and improving risk management practices. This section provides a structured approach to address risk across different organizational levels and contexts systematically.
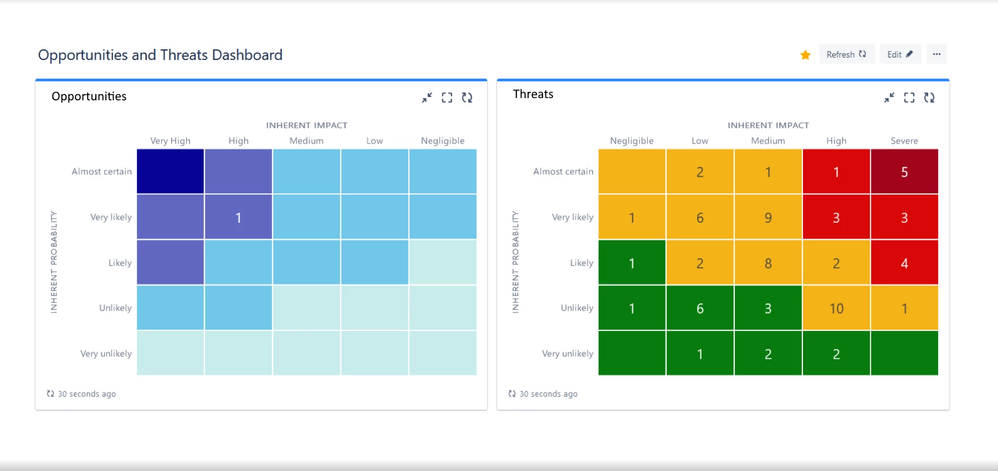
Risk Register by ProjectBalm
Section 5 of the standard encourages organizations to adopt "tools to be used for managing risk." This is one reason we created Risk Register by ProjectBalm.
Our goal was to automate best practice risk management techniques, and do so via an elegant, usable interface that works with you, and not against you. Risk Register will help you to identify, analyse, treat and monitor risks more easily and effectively than ever before.
If you are experienced at risk management, you will find in Risk Register a tool that works the way you want it to work. If you are new to risk management, our documentation and videos will take you through the whole risk management process, giving lots of useful examples.
Risk Register is fully compatible with risk management standards such as ISO 31000, and can also be used for governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) programs such as Sarbanes-Oxley and PCI. And, of course, Risk Register allows you to easily distinguish between opportunities and threats.
Over the last few years, we've grown to become the most popular risk management solution in the Jira marketplace and we are now an Atlassian Platinum Partner. Why not try out Risk Register by ProjectBalm for yourself?
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Craig Schwarze _ProjectBalm_
About this author
Founder at ProjectBalm
ProjectBalm
Sydney
8 accepted answers
3 comments