Create
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Community resources
Community resources
Community resources
How to manage testing and requirements in RTM
November 4, 2025 edited
In modern software development, maintaining control over requirements and testing processes is essential for delivering high-quality products and meeting user expectations.
I'd like to share practical QA techniques and configurations to streamline and standardize testing activities.
It covers workflow in Requirements and Test Management (RTM), from organizing requirements and designing test cases to analyzing results and integrating with issue tracking ↘️
👩💼Manage Requirements
- Group Requirements by feature in folders - helps new team members quickly understand the product.
- Create Test Cases and link them to Requirements (stories) or project tasks - allows you to track the coverage of Requirements in reports.
✍️Create and organize Test Cases
- Use the Page Object pattern to describe Test Cases - this ensures consistency and high-quality test documentation. To apply this approach, organize your test cases into folders.
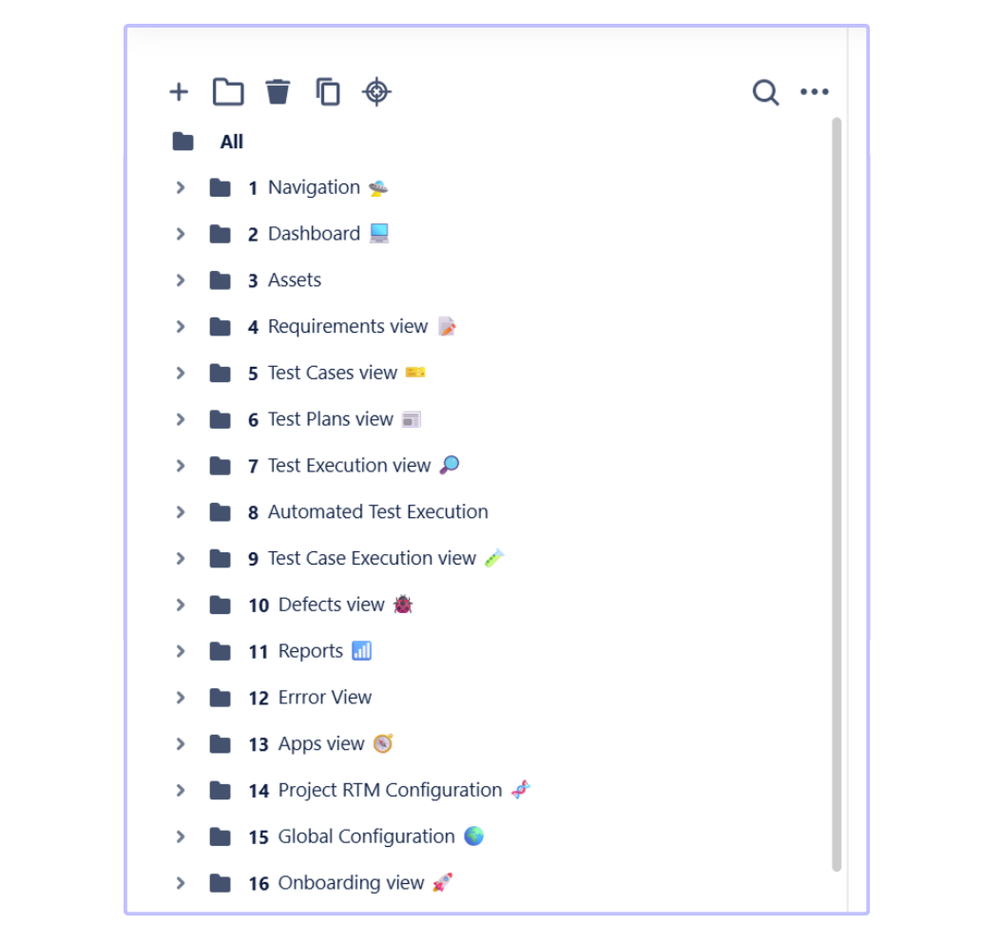
💡You can structure the folders to reflect your application’s views (for example, onboarding, login panel). - Use nested folders and emojis to improve readability and navigation. Emojis visually identify folder contents.
- Add tags in Test Case titles - use brackets (for example, [Login]) to indicate the app view, which helps filter tests during Test Execution.
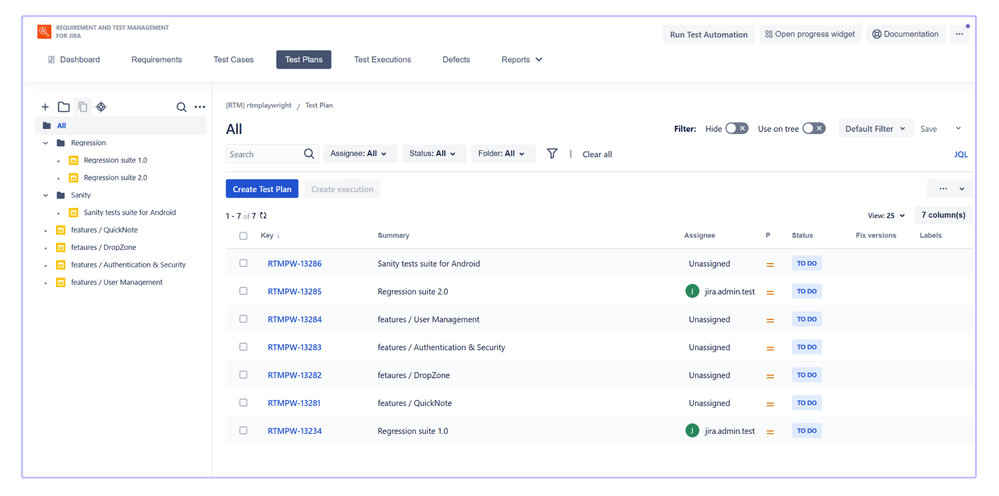
📂 Organize Test Plans
- Use Test Plans to group Test Cases - individual Test Cases can be reused across multiple Test Plans based on scope or testing goals.
- Examples of Test Plan usage by scope of testing:
- Sanity Test Plan - includes key tests of the application’s main views, verifying overall functionality.
- Regression Test Plan - includes detailed and in-depth tests of the entire application.
- Automated Test Plan - includes test cases that have been automated and are used in end-to-end (E2E) testing.
- Dedicated Test Plans - created for specific features or releases, for example, Test Plan: Release No. X / Feature Name.
- Assign a Test Plan to an application version - use the Fix versions or Affect versions field, depending on your project configuration. This lets you easily report progress for each release.
- Create various Test Plans (for example, sanity, regression tests) to better control test coverage.
- Separate manual and automated tests to improve planning and execution.
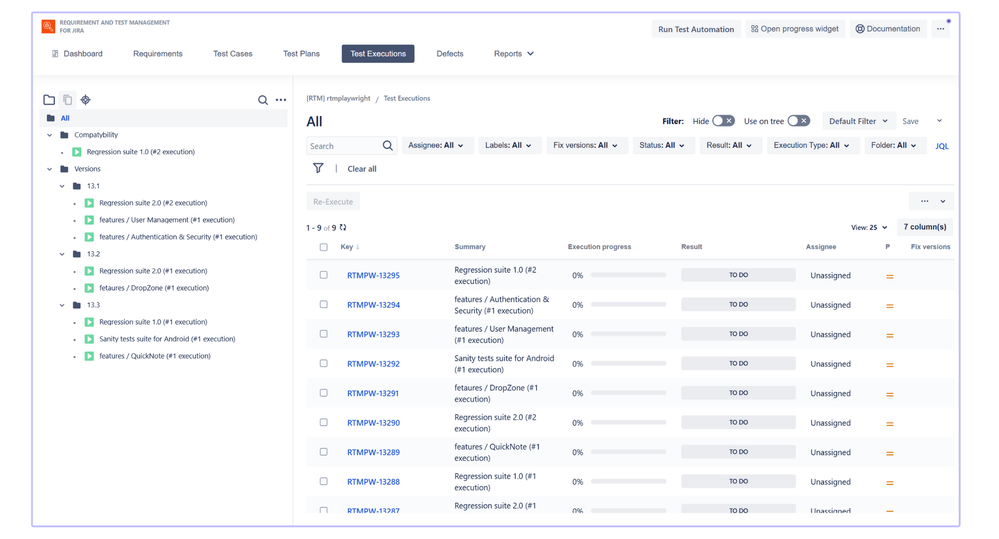
🧪Execute tests and analyze results
- Create Test Executions based on Test Plans - group them into folders by version, for example, Release X.
- Group Test Executions by version - this lets you quickly identify problematic releases. You can also group Test Executions by sprints to easily analyze the quality of each release.
- Categorize defects by version in the Defect Tree in RTM - this allows you to effectively monitor bugs and their impact on specific releases.
- Use comments and change history in tests - this helps you track who made changes and why.
🐞Integrate and track defects
- Link Jira issues (for example, support tickets with bugs and Requirements) - that improves collaboration between teams and increases process transparency.
- Link defects to the tests that detected them - this simplifies product quality analysis.
- Link Defects with Requirements - this shortens the analysis process and facilitates communication with developers. RTM automatically creates this association if you previously linked the Test Case to a Requirement.
- Mark the defect’s priority, version, and status - this enables effective defect backlog management.
By applying these practices, teams can ensure traceability, improve collaboration, and increase overall process efficiency 🙌
Was this helpful?
Thanks!
Weronika Hałdaś_Deviniti_
Atlassian Partner
TAGS
Atlassian Community Events
Copyright © 2026 Atlassian
0 comments